The odds ratio (OR) is a ratio of 2 numbers, like the relative risk we have 3 options OR = 1 The odds in the first group are the same as those in the second So no evidence that drinking wine can either OR > 1 The odds of having the disease in the exposed group areRelative Risk, Odds, and Fisher's exact test I) Relative Risk A) Simply, relative risk is the ratio of p 1/p 2 For instance, suppose we wanted to take another look at our Seat belt safety data from Florida Safety equipment Injury in use Fatal Nonfatal Total None 1,601 165,527 167,128 Seat belt 510 412,368 412,878Pretend there is a drawing with one winner and 10,000 people entered The odds of winning are 1/9,999 () and the probability of winning is 1/10,000 () In this case, odds and probability are essentially identical Relative Risk (RR) & Odds Ratio (OR)
Plos One Farm Exposure As A Differential Risk Factor In Anca Associated Vasculitis
Odds ratio vs risk reduction
Odds ratio vs risk reduction-17/8/18 · Before we look at odds and risk ratios, let's be clear on what odds and probabilities are (this couple of paragraphs added on August 18) A probability will be a familiar concept to readers of this blog Let's say that one quarter of tigers are diseased27/10/17 · Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently (



Statistc 111 Lecture Notes Spring 19 Lecture 11 Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ert2
7/2/14 · Researchers investigated the effectiveness of a probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus for the prevention of any diarrhoea associated with antibiotic use in hospital A randomised double blind placebo controlled trial study design was used The intervention consisted of the probiotic drink twice a day during a course of antibiotics and for one week afterwards27/8/15 · Odds Ratios vs Risk Ratios Posted on August 27, 15 September 25, 15 by StatsBySlough From the previous post , we understand that Odds Ratios (OR) and Risk Ratios (RR) can sometimes, but not always be interpreted in the same wayRisk (Retrospective) Menu location Analysis_Clinical Epidemiology_Risk (Retrospective) This function calculates odds ratios and population attributable risk with confidence intervals You can examine the likelihood of an outcome such as disease in relation to an exposure such as a suspected risk or protection factor
Nevertheless, odds and risks are not mathematically equivalent but may converge under certain conditions Notably, unlike risks, odds are not probabilitiesThe difference between odds ratio and risk ratio May 15, 14 • ericminikel The other day I was emailing with a statistical genetics colleague about a rare SNP associated with a phenotype I stated that the minor allele frequency (MAF) was 07% in cases and 01% in controls, for a risk ratio of 7 After clicking send, I felt a twinge of regret14/12/14 · The relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1125, while the odds ratio is about 225 The reasons a medical article might choose one method of reporting over the other are complex, but the message here is that sorting that out starts by being clear about the difference between probability and odds
MEDICINA BASADA EN EVIDENCIAS Odds ratio aspectos teóricos y prácticos Odds ratio Theoretical and practical issues Jaime Cerda 1,2, Claudio Vera 1,3, Gabriel Rada 1,4 * 1 Unidad de Medicina Basada en Evidencia 2 Departamento de Salud Pública 3 División de Obstetricia y Ginecología 4 Departamento de Medicina Interna Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia UniversidadRisks and Odds When talking about the chance of something happening, eg death, hip fracture, we can talk about • risk and relative risk or • odds and odds ratio Risks and odds Risks and odds Risks A proportion Numerator / Denominator Odds A ratio Numerator / (DenominatorRelative Risk and Odds Ratios are both methods of comparing the likelihood of an outcome occurring between two groups The difference, and particularly the concept of odds ratios, are commonly confused Relative risk tends be much more intuitive than odds ratios Imagine a trial has been performed, where group A was exposed group



Statistc 111 Lecture Notes Spring 19 Lecture 11 Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ert2


Plos Medicine Childhood Stunting In Relation To The Pre And Postnatal Environment During The First 2 Years Of Life The Mal Ed Longitudinal Birth Cohort Study
Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio In clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample,8/1/16 · Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 tableIn biomedical research, we are often interested in quantifying the relationship between an exposure and an outcome "Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube



Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
The odds ratio (OR) and relative risk (RR) are measures of association for dichotomous nominal variables The OR has been widely used for biomedical research, the reasons for this are 1) The OR determines an estimate (with confidence interval) for relations between binary dummy10/6/18 · Risk and Odds Risk vs odds The terms 'risk' and 'odds' are often used interchangeably but they actually have quite different CER = 02 EER = 100 / 1000 EER = 01 RR = 01 / 02 ARR = 02 – 01 ARR = 01 RRR = 01 / 02 RRR = 05 NNT = 1 / 01 Dr Marc Barton qualified from9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects


Plos One The Impact Of Weather On Women S Tendency To Wear Red Or Pink When At High Risk For Conception



Use Of Normal Risk To Improve Understanding Of Dangers Of Covid 19 The Bmj
21/1/03 · Odds provide a measure of the likelihood of a particular outcome They are calculated as the ratio of the number of events that produce that outcome to the number that do not Odds are commonly used in gambling and statistics Odds can be demonstrated byRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter4/5/09 · Relationship of the odds ratio to the risk ratio according to 4 levels of outcome risk (cumulative incidence) for an average exposed and unexposed subject01,10,25, and50 Estimates assume the number of exposed subjects is equal to the number unexposed Figure 4



Against The Odds What Is Your Risk Of Getting An Std Through A One Off Heterosexual Encounter



Risk Factors For Severe Illness And Death In Covid 19 A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Medrxiv
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,Rather the odds is threefold greaterIn the "risk" of response and a 60% increase in the "risk" of remission Risk, therefore, is used to reflect probability, regardless of the desirability or undesirability of an event 2 Relative risk is an important and commonly used Odds Ratio



When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj


Plos One Farm Exposure As A Differential Risk Factor In Anca Associated Vasculitis
Odds ratio vs risk ratio Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an The difference In any case, RR and OR values are similar when the frequency of the effect is low, below 10%, although We're leaving And here weSo even from this simple case we see that the risk varies from 0 to 1 and the odds vary from 0 to infinity In fact, if Risk (or p) < 05, OR < 1;The difference between odds and risk is small when the event is rare (as illustrated in the first example above where a risk of 0091 was seen to be similar to an odds of 01) When events are common, as is often the case in clinical trials, the differences between odds and risks are large For example, a risk of 05 is equivalent to an odds of 1;
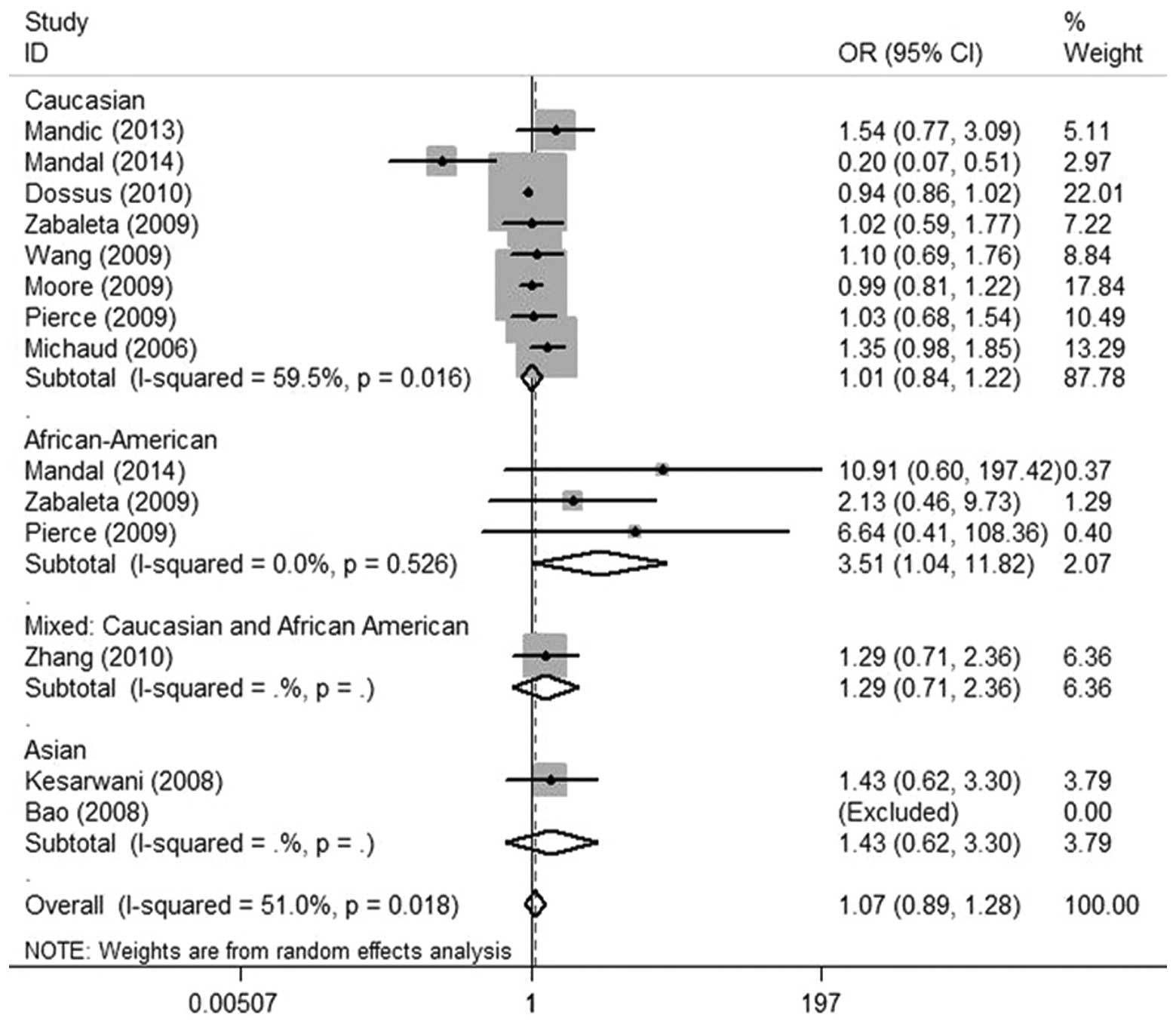


Association Of Interleukin 6 174 G C Polymorphism With The Prostate Cancer Risk A Meta Analysis



Prevalence And Odds Or Of Cardiovascular Risk Factors For Each Sleep Download Table
Cases 1 and 4 have the same absolute risk reduction, NNT, and odds ratios, but very different relative risk, relative risk reduction, and risk at baseline Real Example The following example 18 is a prospective study, which compares the incidences of dyskinesia after ropinirole (ROP) or levodopa (LD) in patients with early Parkinson's diseaseRisk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;11/7/16 · The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio)



Odygj4kbrv3cm



Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
3 RELATIVE VS ABSOLUTE RISK (ODDS) Now that we have delineated the distinction between risk and odds, we will address a second point of confusion concerning these calculations absolute and relative risk (Note that "odds" can replace "risk" in each instance discussed in this paragraph and also in the Concluding Comments section)The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to the treatment Odds is the number having the outcome divided by the number not having the outcome28/9/ · Risk Ratio = CI e /CI u = 090/058 = 155 Interpretation Smokers had 155 times the risk of respiratory disease compared to nonsmokers over an 18 year period of observation Using the same cumulative incidences we can calculate the risk difference, an absolute measure of association Risk Difference = CI e CI u = 090 058 = 032 = 32



Tottenham Vs Wolfsberger Betting Odds Offers Tips Get Risk Free Bet On Europa League Tie Plus 16 1 Bet Builder


Gun Violence Data Odds Of Being Shot Other Causes Of Death Compared
10/1/13 · Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect sizeRisk (AR) for each group It is analogous to the odds ratio (OR) when events are rare Relative risk is calculated as the absolute risk (AR) in the intervention group divided by the AR in the control group It would seem that the claim above about HR and RR is generally accepted as correct, although we couldn't find any derivation supporting itMany sites which discuss Risk Probabilities sum together the 14 and 777 to give a 2611 probabality for each winning only one battle It's interesting to note that by using the H(N) values for the "highest" of three dice, along with the "N or less" figures for both i=2 and i=3 Not very good odds



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence


Plos One Modifiable Risk Factors For Alzheimer Disease And Subjective Memory Impairment Across Age Groups
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsOdds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to noneventsQuestion 23 from the second paper of 08 asked the candidates to define effect size Effect size is a quantitative reflection of the magnitude of a phenomenon;



Pairwise Comparisons Of Selected Risk Factor Effects Between Skin Download Table



Ppt Exploratory Data Analysis With Two Qualitative Variables Powerpoint Presentation Id
When it comes to analytical studies like cohort studies and case control studies, these two words odds ratio and relative risk, may get confused with each other sometimes, especially for beginnersBoth are just two distinct terms used to denote "strength of association"If Risk = 1, OR = InfinityOdds ratio and relative risk About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features © 21 Google LLC



Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



Data Analysis For The Bsc Year Ppt Download
Odds and Odds Ratios Odds are the probability of an event happening / the probability of an event not happening Thus the odds of throwing a three with one die is 1/5 odds = probability / (1 probability) and conversely probability = odds / (1 odds) Odds Ratio Odds ratio is the ratio of odds for the exposed group vs the unexposed group1/1/16 · Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR),Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)
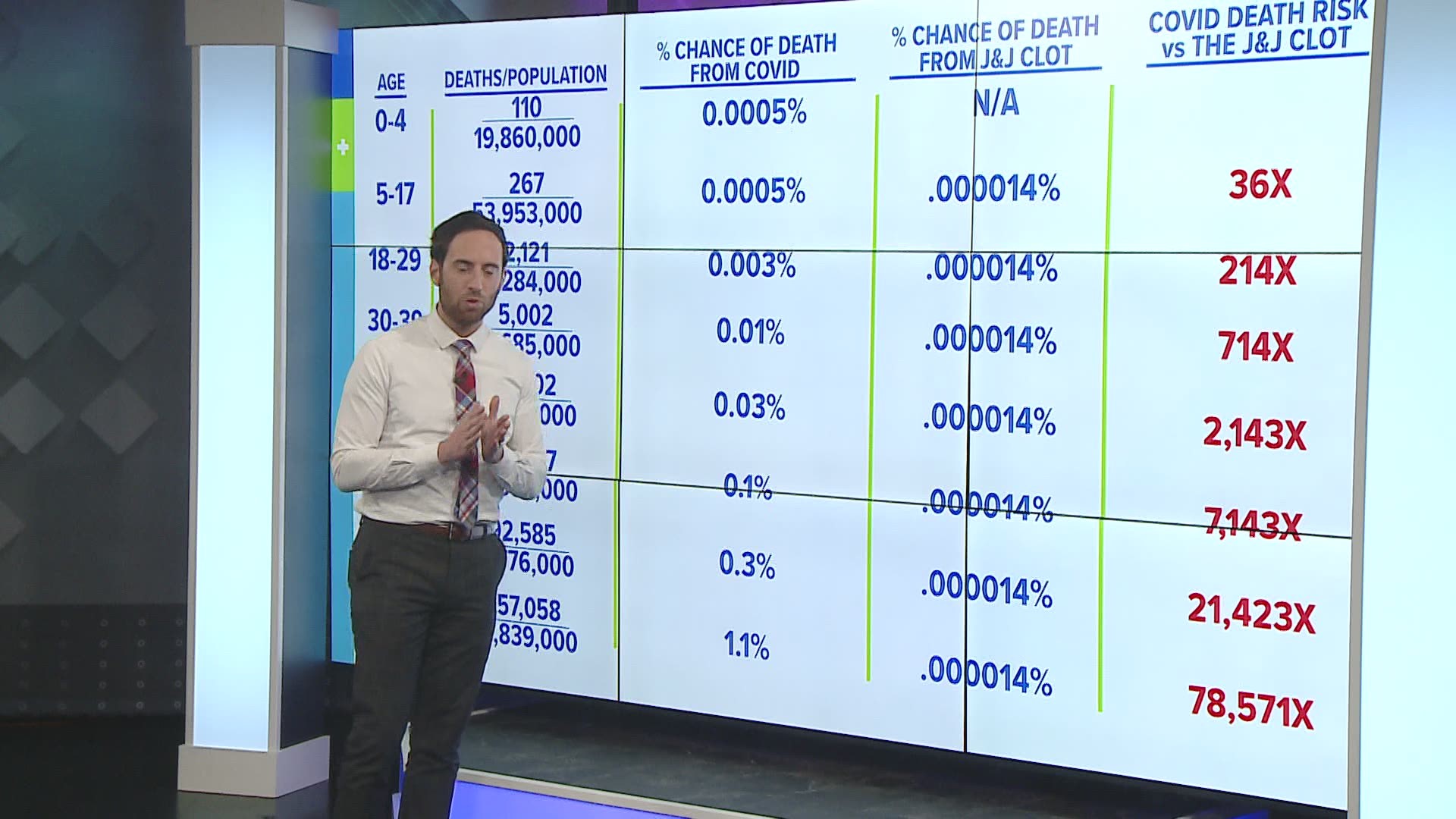


Aedbtsrtz2g 0m


Epidemiology Stepwards
And a risk of 095 is equivalent to odds of 19If Risk = 05, OR = 1;Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3 against



Pgy5rhc0ple3ym



Adjusted Odds Ratios 95 Ci Of Risk Factors Associated With Last Year Download Scientific Diagram
For example, the magnitude of the positive effects of a drug on the study population Measures of effect size include absolute risk, relative risk, odds ratio and numbers needed to treat (NNT)



Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia
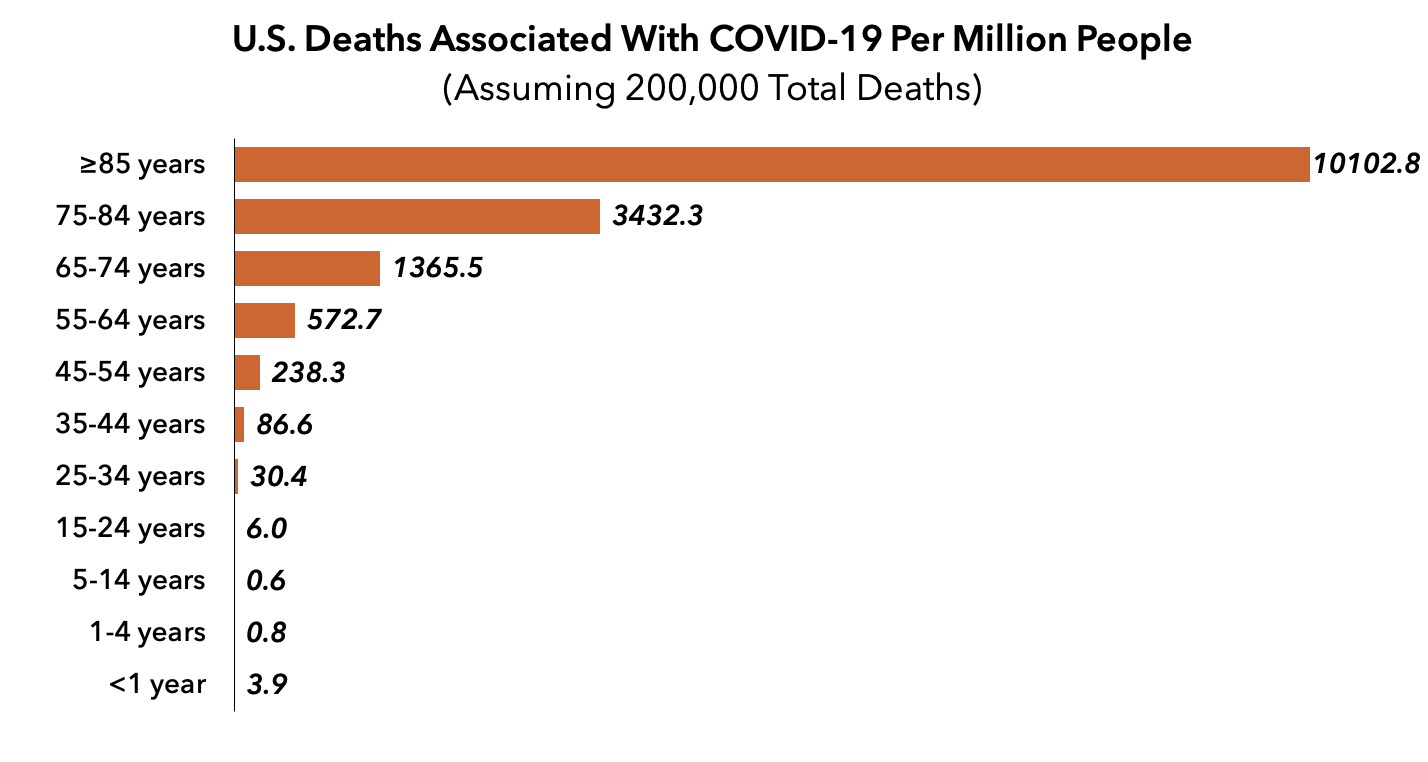


The Chances Of Dying From Covid 19 By Avik Roy Freopp Org



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Case Control Studies Statistics Ppt Download



Popm 3240 Lecture Notes Winter 16 Lecture 9 Confidence Interval Relative Risk Cohort Study
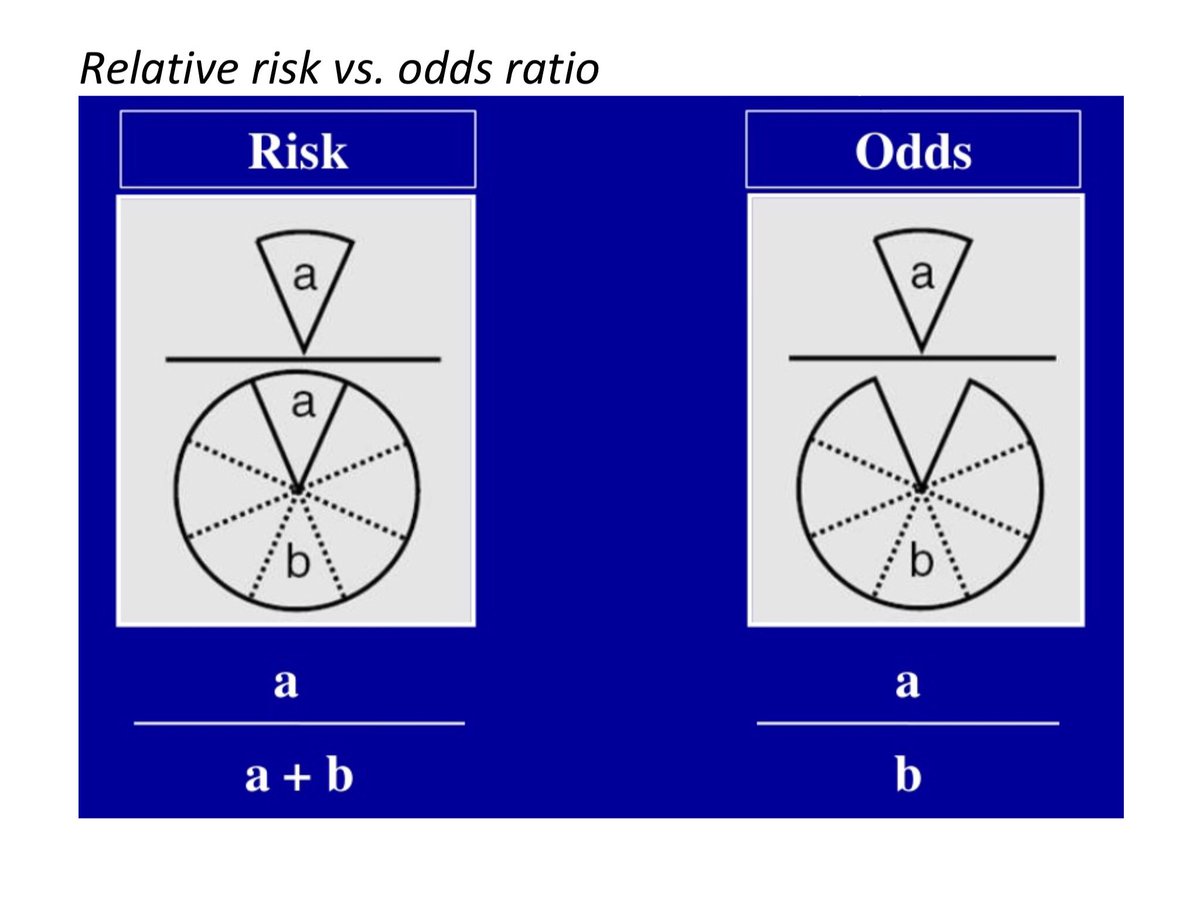


Bryan Carmody For M2s Preparing For Usmle Step 1 Epidemiology Questions Are Free Points You Don T Have To Make 2x2 Tables Or Memorize Formulae From First Aid To Calculate Or
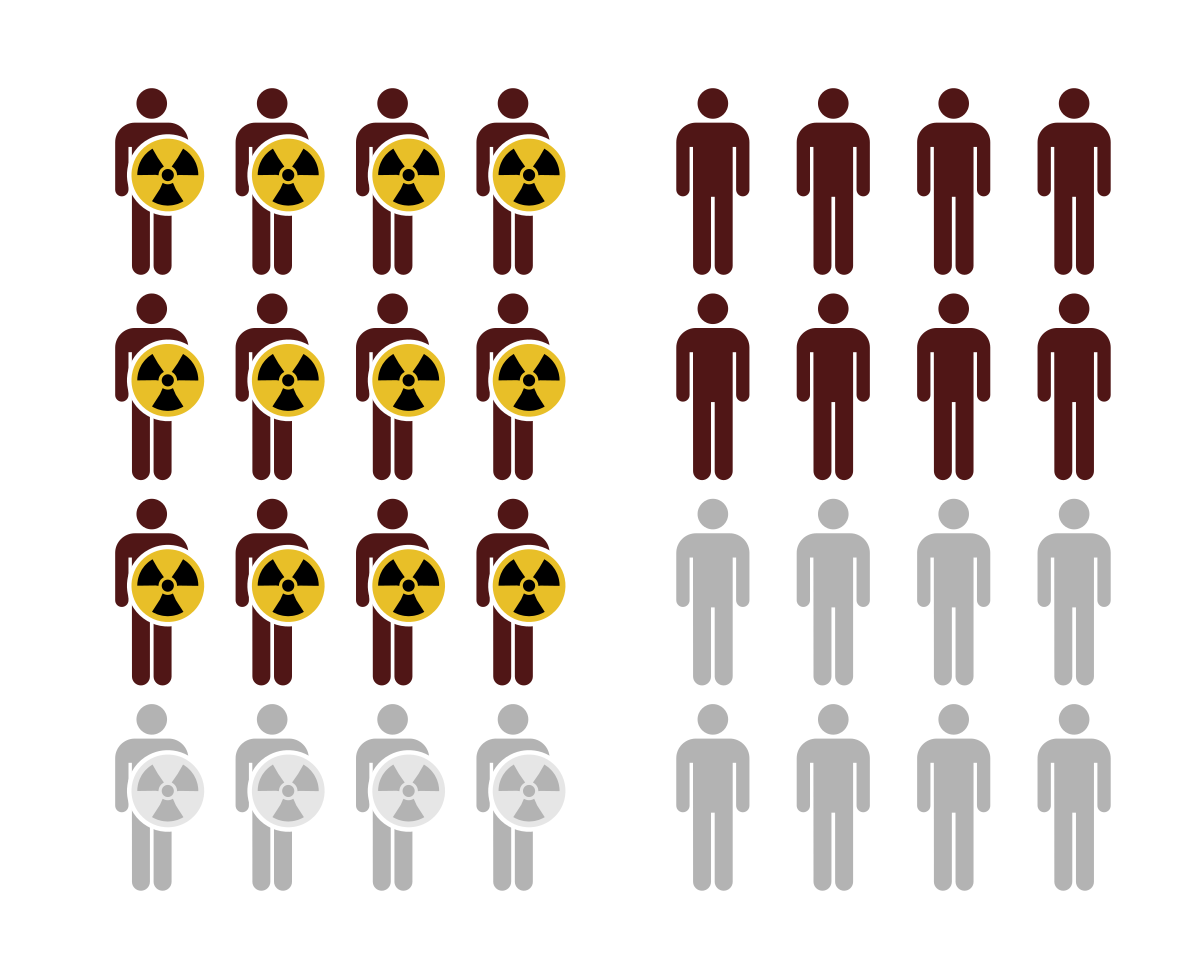


Attributable Fraction Among The Exposed Wikipedia



Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube


Plos One Extra Vitamin D From Fortification And The Risk Of Preeclampsia The D Tect Study



Your Risk For Covid 19 Memorial Hermann



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube



Forest Plot Of Odds Ratio Or And 95 Confidence Interval Ci For Each Study Of The Association Between The 1131t C Polymorphism And Metabolic Syndrome Risk Under Dominant Model Carriers Vs Non Carriers In



Solved Iv Estimate And Interpret The Relative Risk Compa Chegg Com


Funnel Plot Of The Risk Of Non Syndromic Cleft Lip Palate Related To Download Scientific Diagram



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence


Risk Of Death By Age And Sex
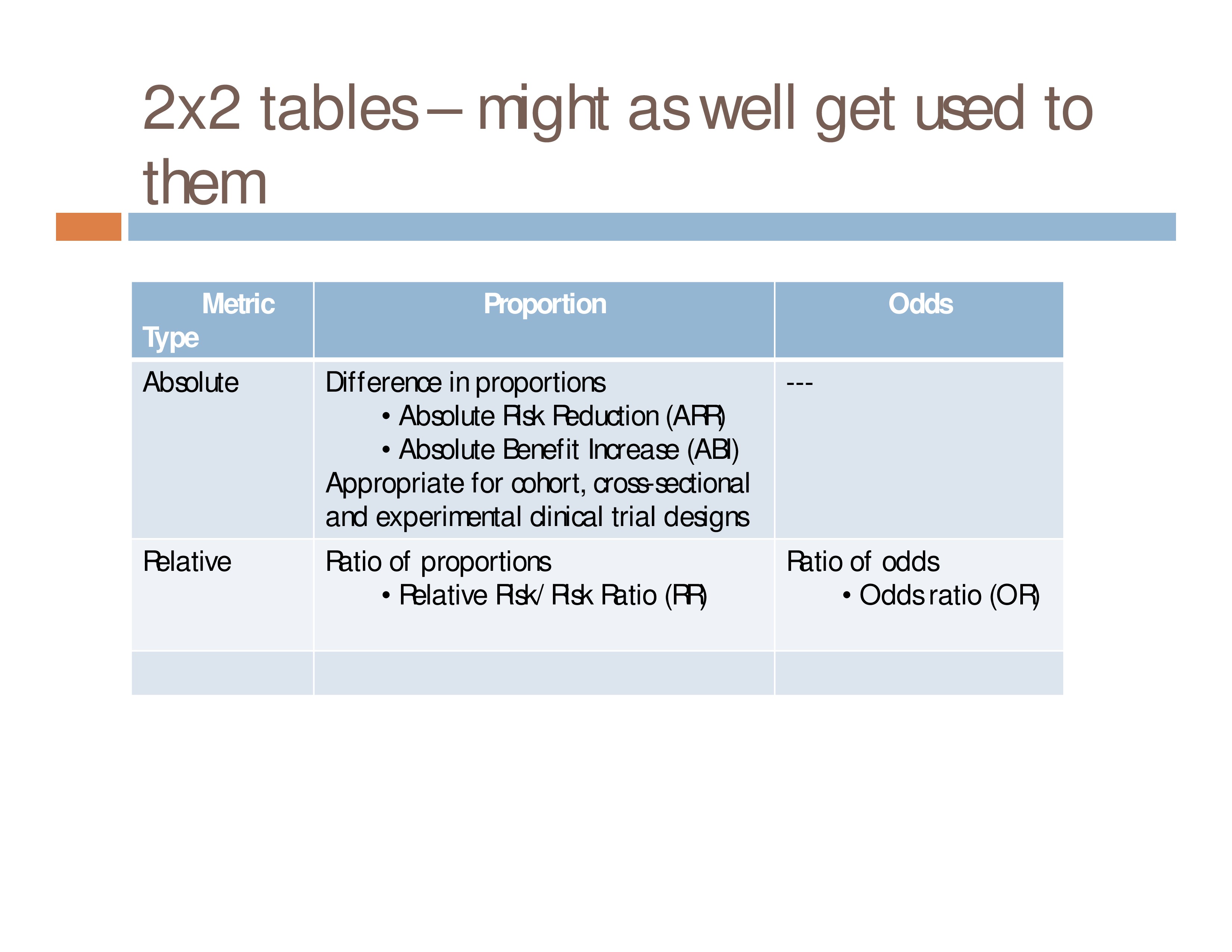


Event Based Measures Of Effect Size Asha Journals Academy



How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube
/risk-factors-and-pregnancy-loss-2371376_FINAL-8330ff11ec7a43f8a3bae1e3181e4847.png)


Risk Factors For Pregnancy Loss
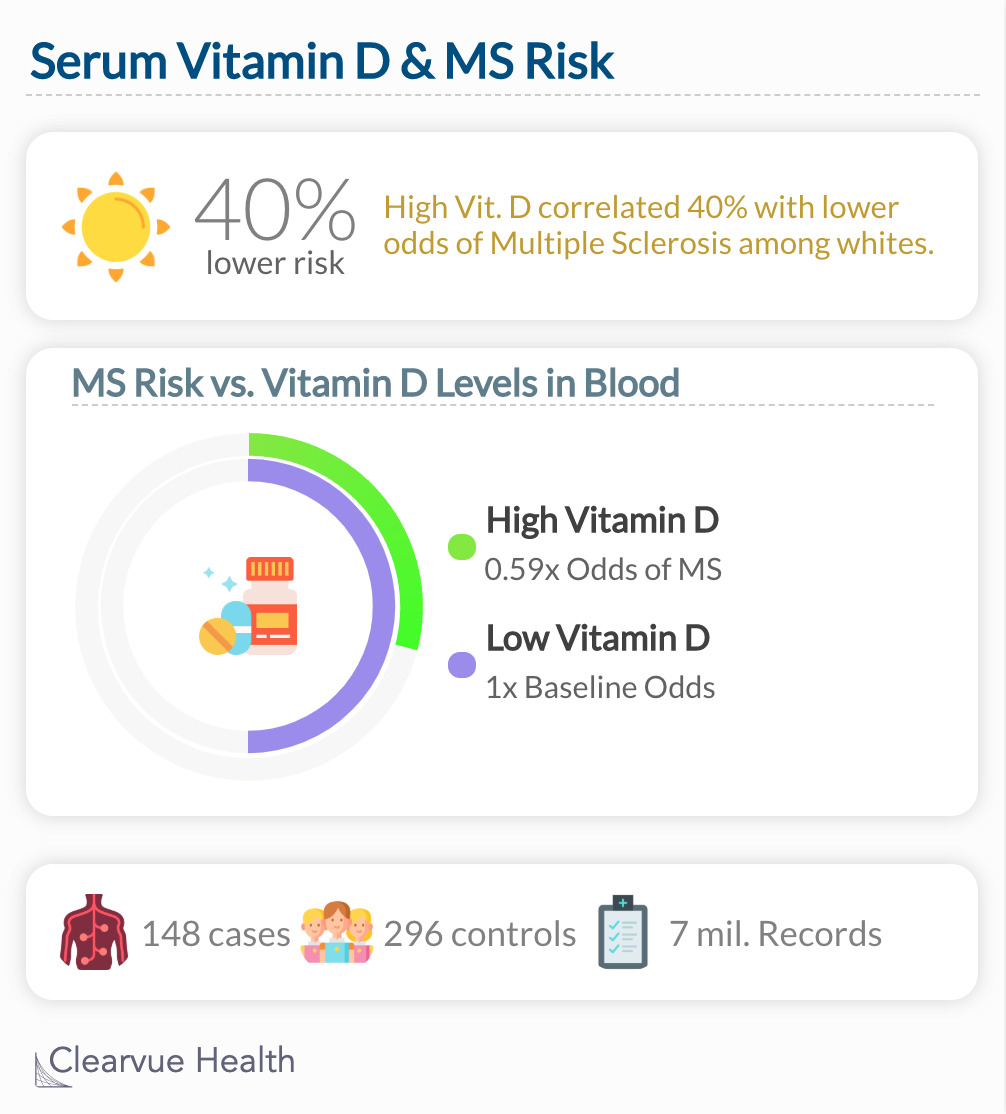


Does The Amount Of Vitamin D You Have Affect Your Odds Of Getting Multiple Sclerosis Infographics



Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Go Member Center Membership Overview Member Benefits Member Directory Napcrg Connect Get Involved Special Interest Groups Career Opportunities Member Newsletter Member Blog Conferences Annual Meeting Overview Registration Call For


Plos One Breast And Bottle Feeding As Risk Factors For Dental Caries A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo
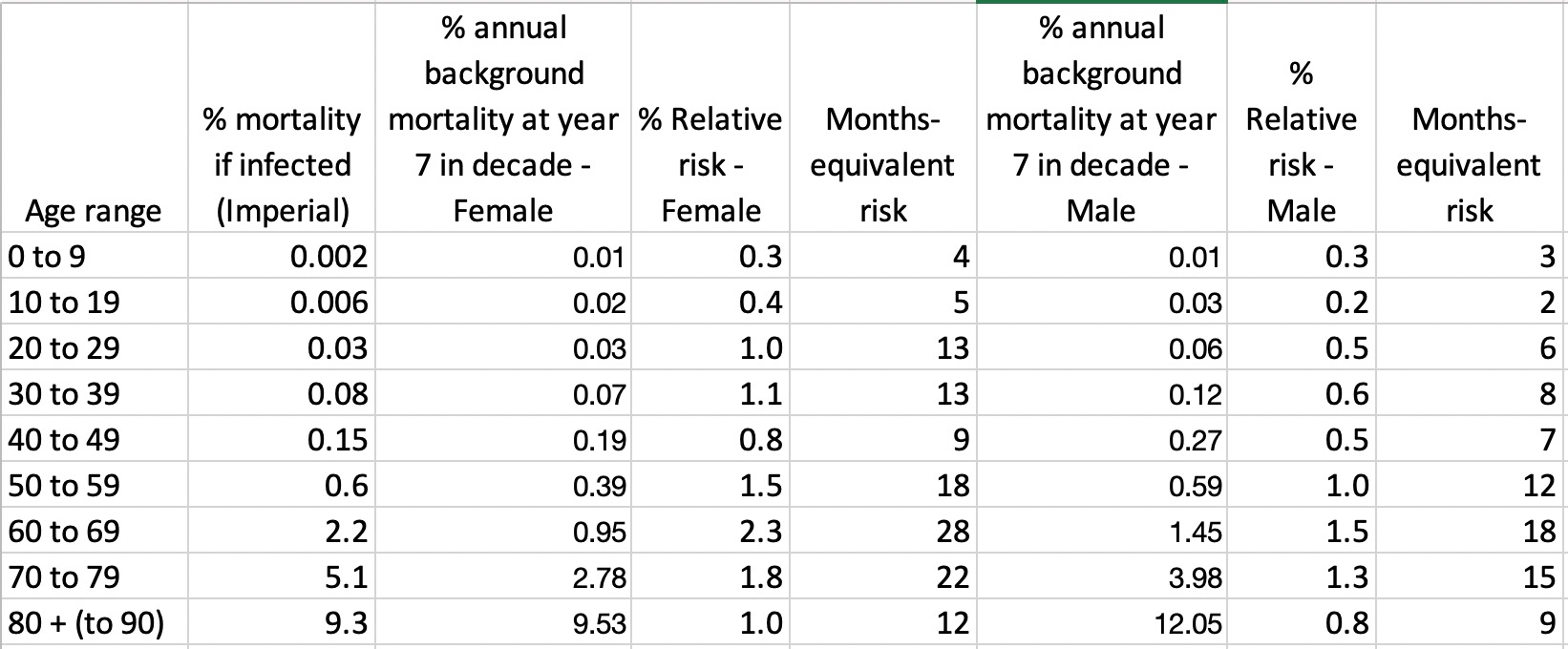


How Much Normal Risk Does Covid Represent By David Spiegelhalter Wintoncentre Medium
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_The_Math_Behind_Betting_Odds_and_Gambling_Nov_2020-01-735accb453c8424b9e063c2c14e4edf4.jpg)


The Math Behind Betting Odds Gambling


Hpv Vaccine Injury Vs Cervical Cancer Risk What Are Your Odds By Fred Lumiere Medium
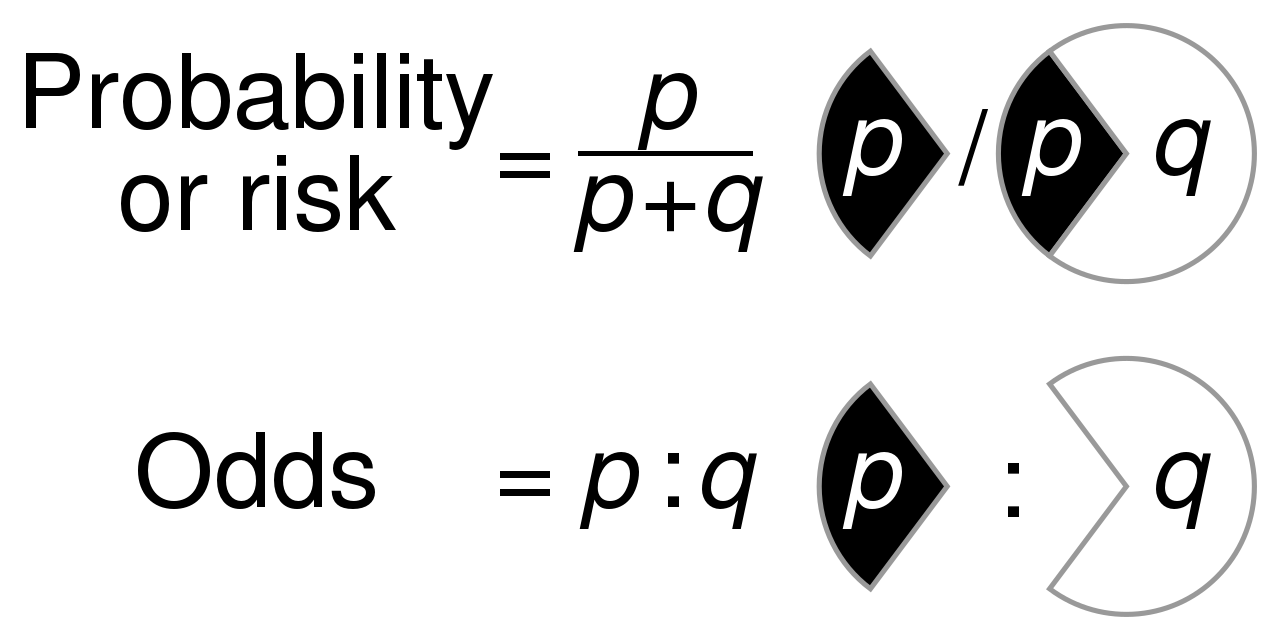


File Probability Vs Odds Svg Wikimedia Commons



Madhu Pai Md Phd Risk Difference Vs Excess Risk Vs Attributable Risk Confused This Handout On Measures In Epi Might Help T Co 6bfzxmbqt8 T Co Uyyjdgtktk
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Understanding_Forex_Risk_Management_Jul_2020-01-44f4b0616f4547ea8cef266cde06cf01.jpg)


Understanding Forex Risk Management


Figure 2 Scientific Reports



Odds Ratio 95 Ci Of Ischemic Stroke For 1th 9th Percentile Vs Download Table



Odds Ratio Or Of Presence Of Sq1 Sq3 Fractures Yes Vs No With Download Scientific Diagram
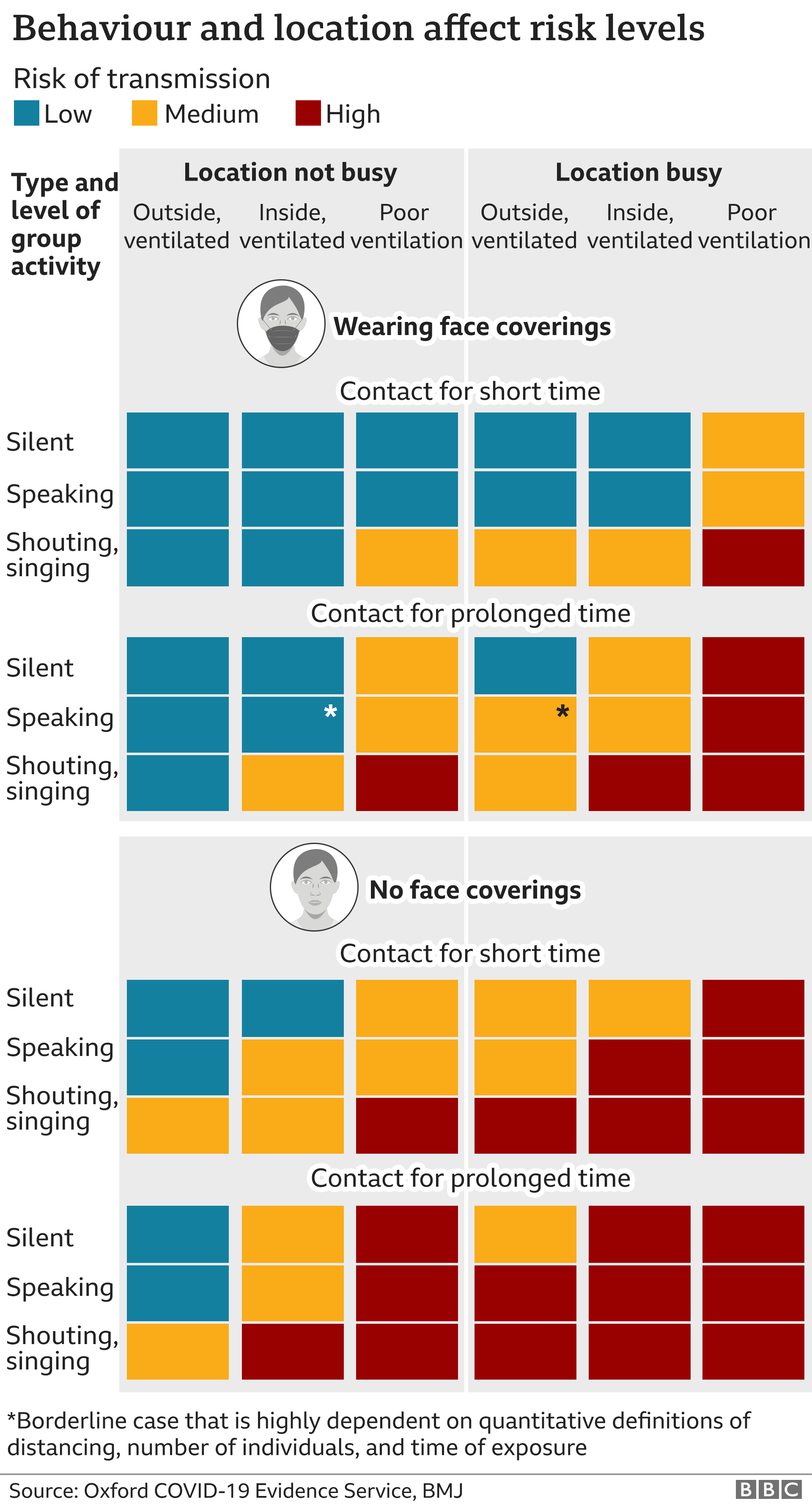


Covid Risk 3 People 3 Very Different Covid Risks What S Yours c News



How Much Normal Risk Does Covid Represent By David Spiegelhalter Wintoncentre Medium



Forest Plot Of Odds Ratios For The Association Between Pcsk9 Rs Download Scientific Diagram
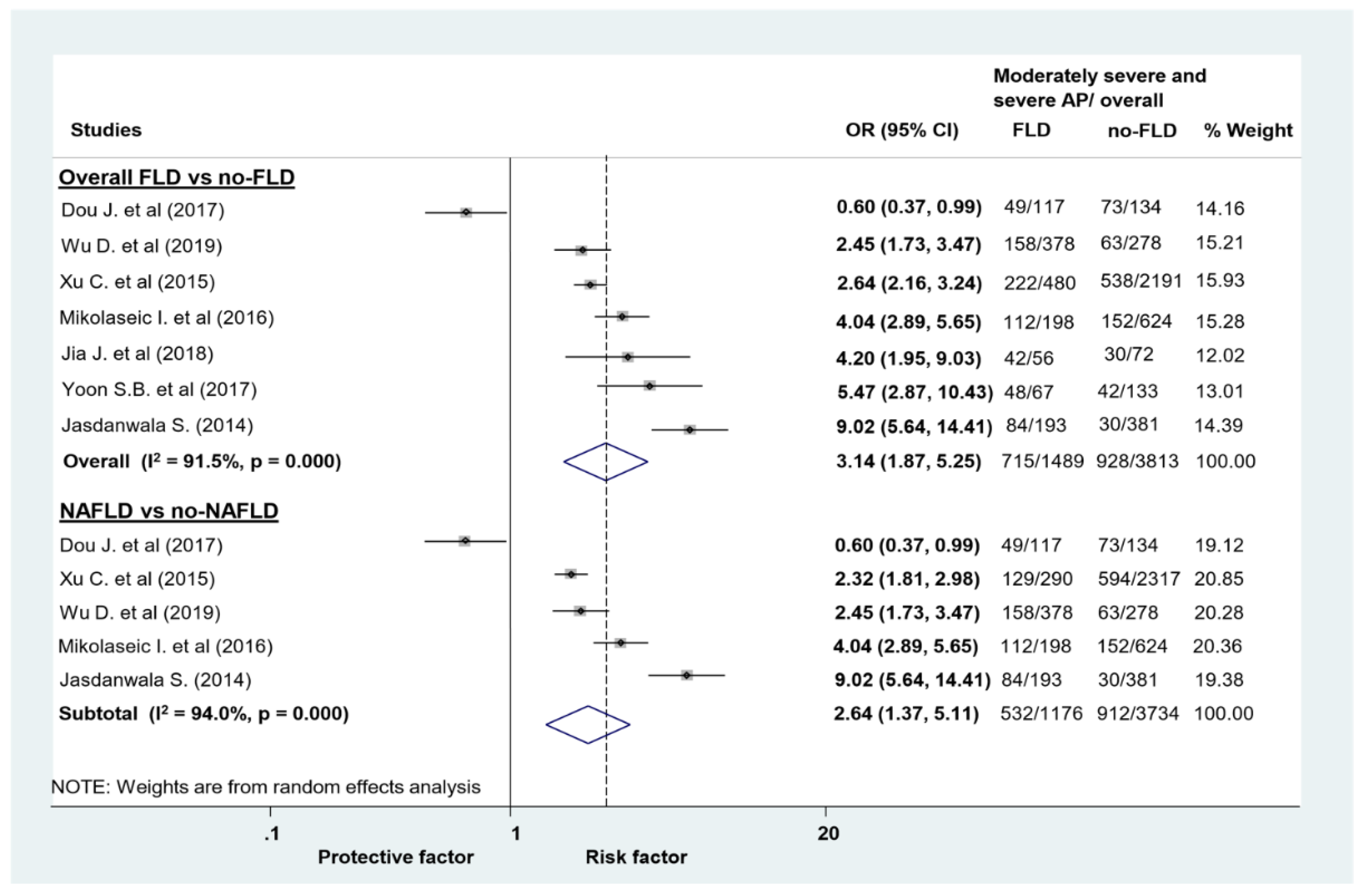


Jcm Free Full Text Fatty Liver Disease And Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Worsen The Outcome In Acute Pancreatitis A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Html


Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies
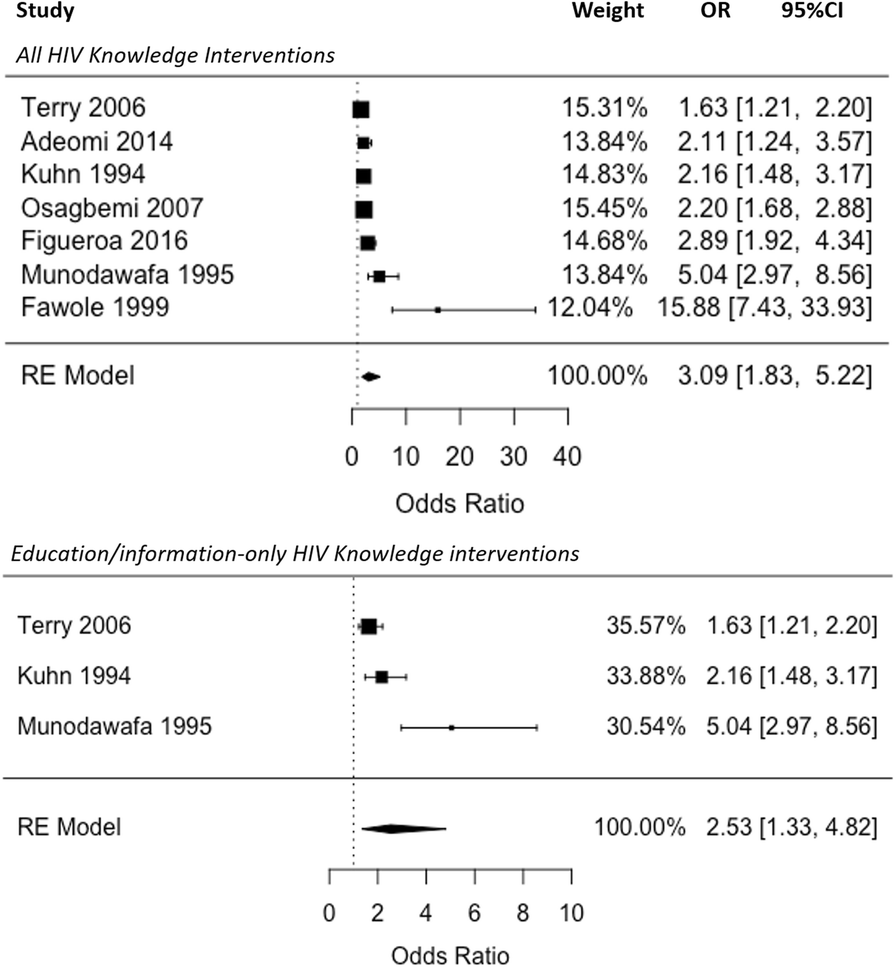


The Effect Of Hiv Educational Interventions On Hiv Related Knowledge Condom Use And Hiv Incidence In Sub Saharan Africa A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Bmc Public Health Full Text



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Current Asthma Meta Analyses Of The Adjusted Odds Ratios Of Asthma At Download Scientific Diagram



Forest Plots Of Odds Ratios For The Association Between Microrna 146a Download Scientific Diagram


Plos Medicine Long Term Trends In Incidence And Risk Factors For Ischaemic Stroke Subtypes Prospective Population Study Of The South London Stroke Register



Absolute Risk Reduction Vs Relative Risk Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Forest Plot Of The Odds Ratio For Achievement Of Rbc Ti In Patients With Low Risk Vs Intermediate 1 Risk
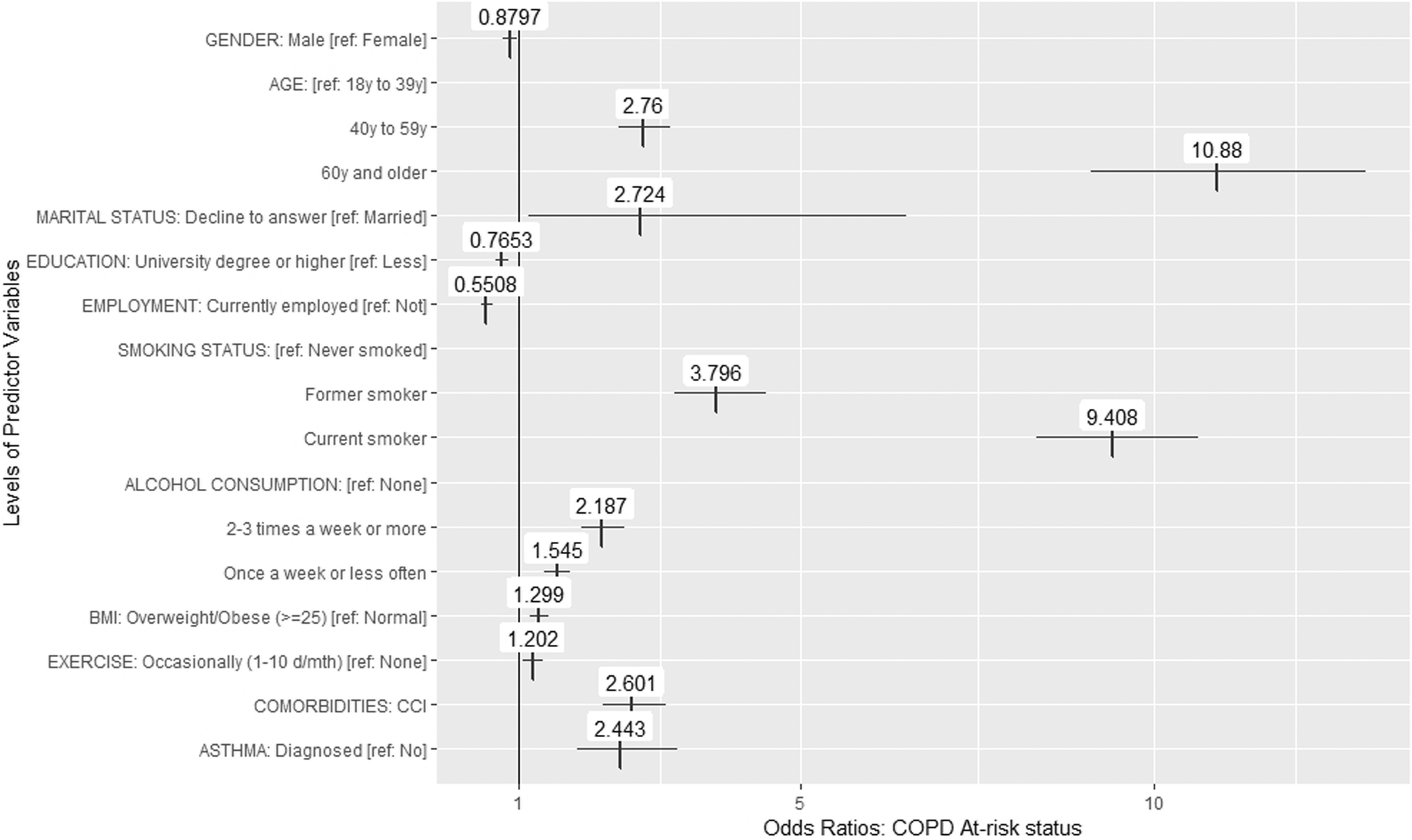


Characteristics And Health Burden Of The Undiagnosed Population At Risk Of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease In China Bmc Public Health Full Text



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube
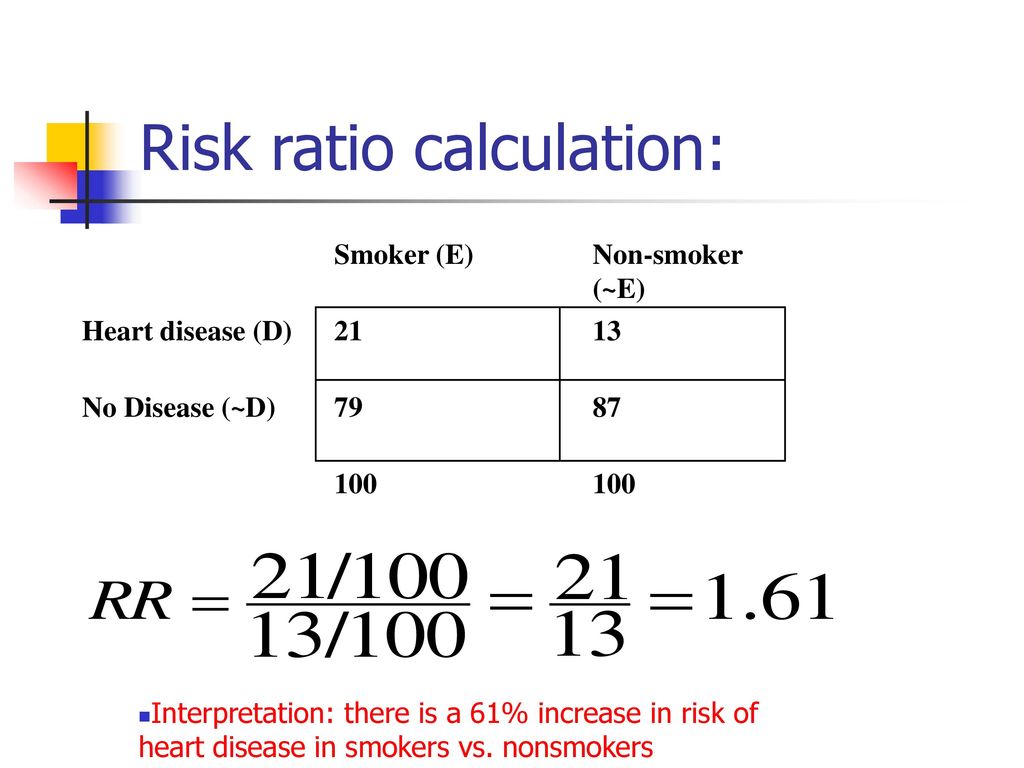


The Binomial Applied Absolute And Relative Risks Chi Square Ppt Download



The Binomial Applied Absolute And Relative Risks Chi Square Ppt Download



Evidence Based Journal Club Intention To Treat Odds And Risk Ppt Download
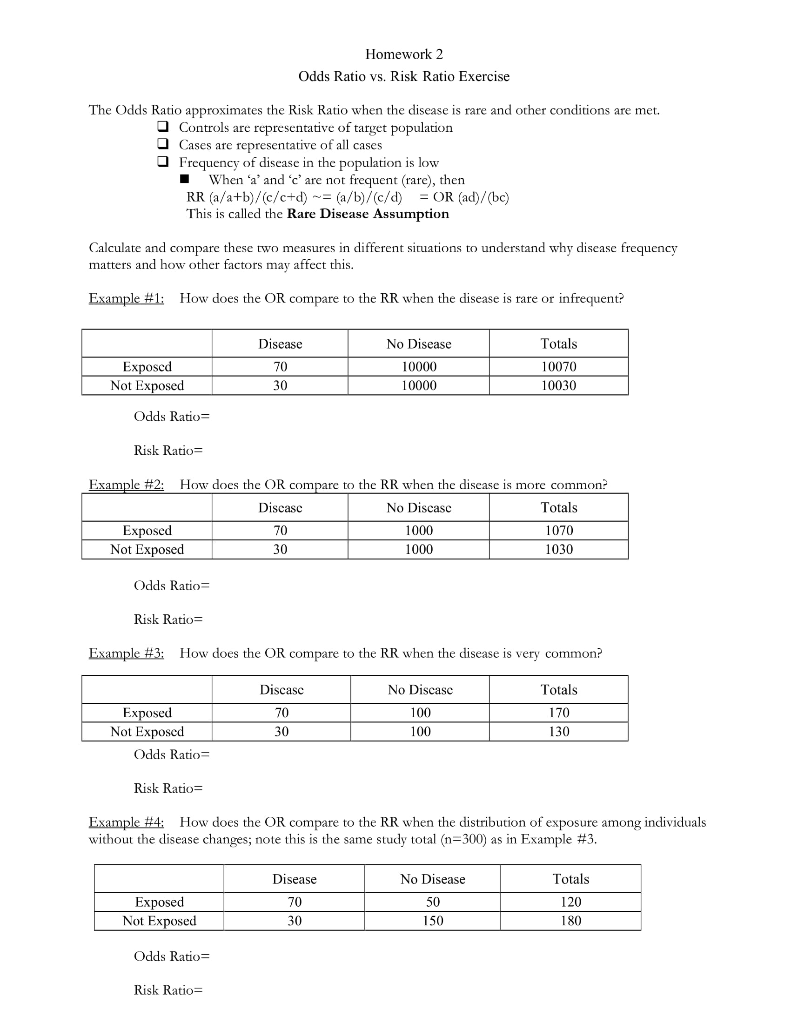


Solved Homework 2 Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Chegg Com



Odds Ratios From Univariate Regression Model Of Oasis Vs Risk Factors Download Table



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios


Risk Of Death By Age And Sex



Tn Sports Betting Florida Gators Vs Tennessee Volunteers Odds



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Extensive Video Youtube
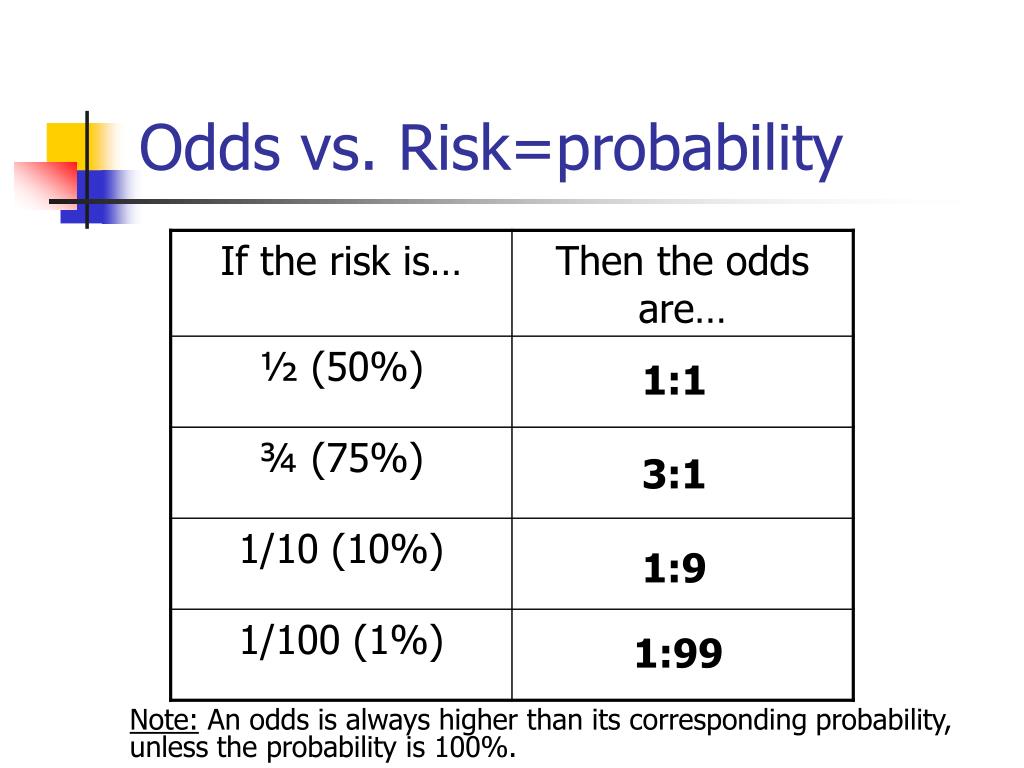


Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough
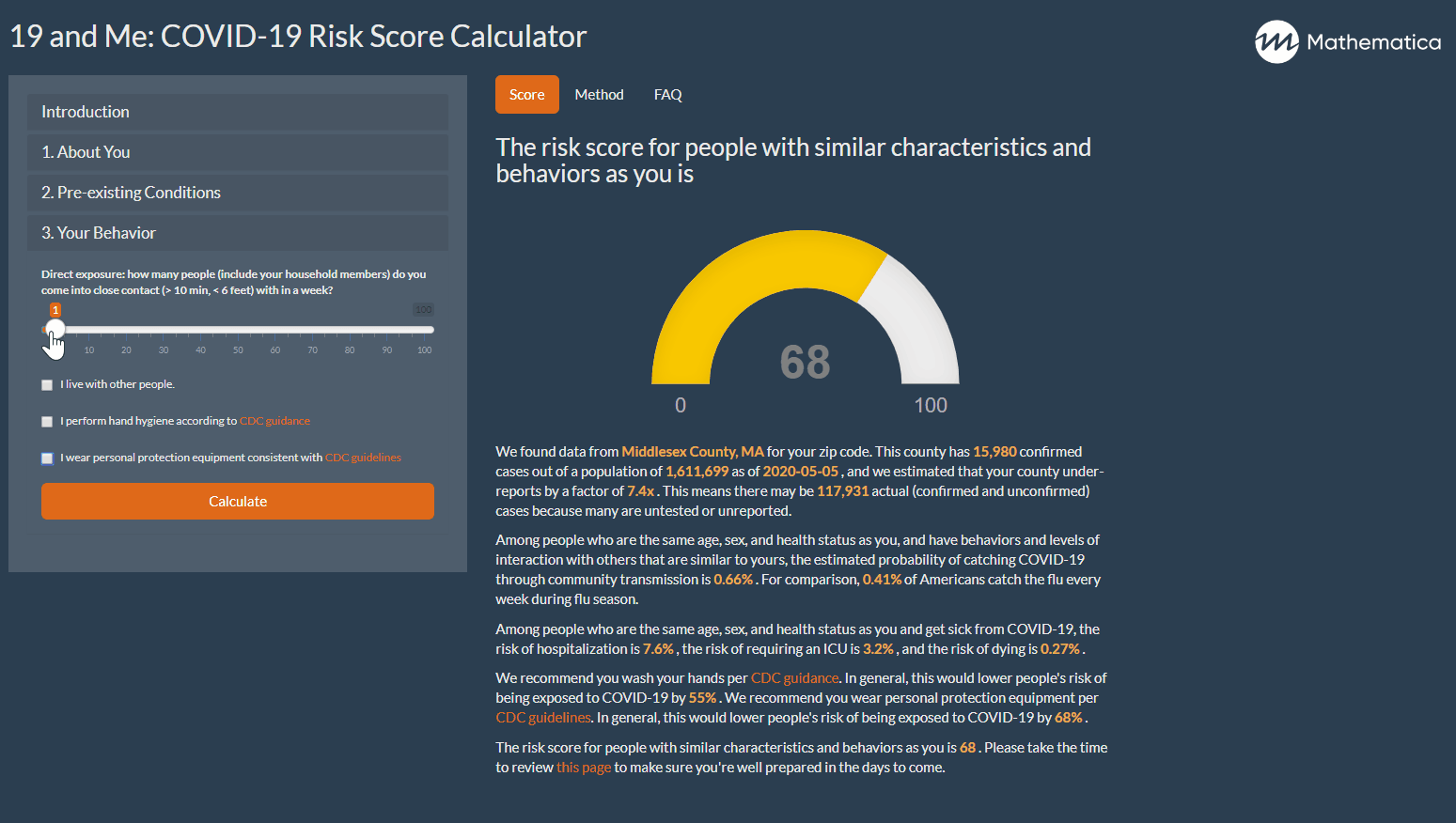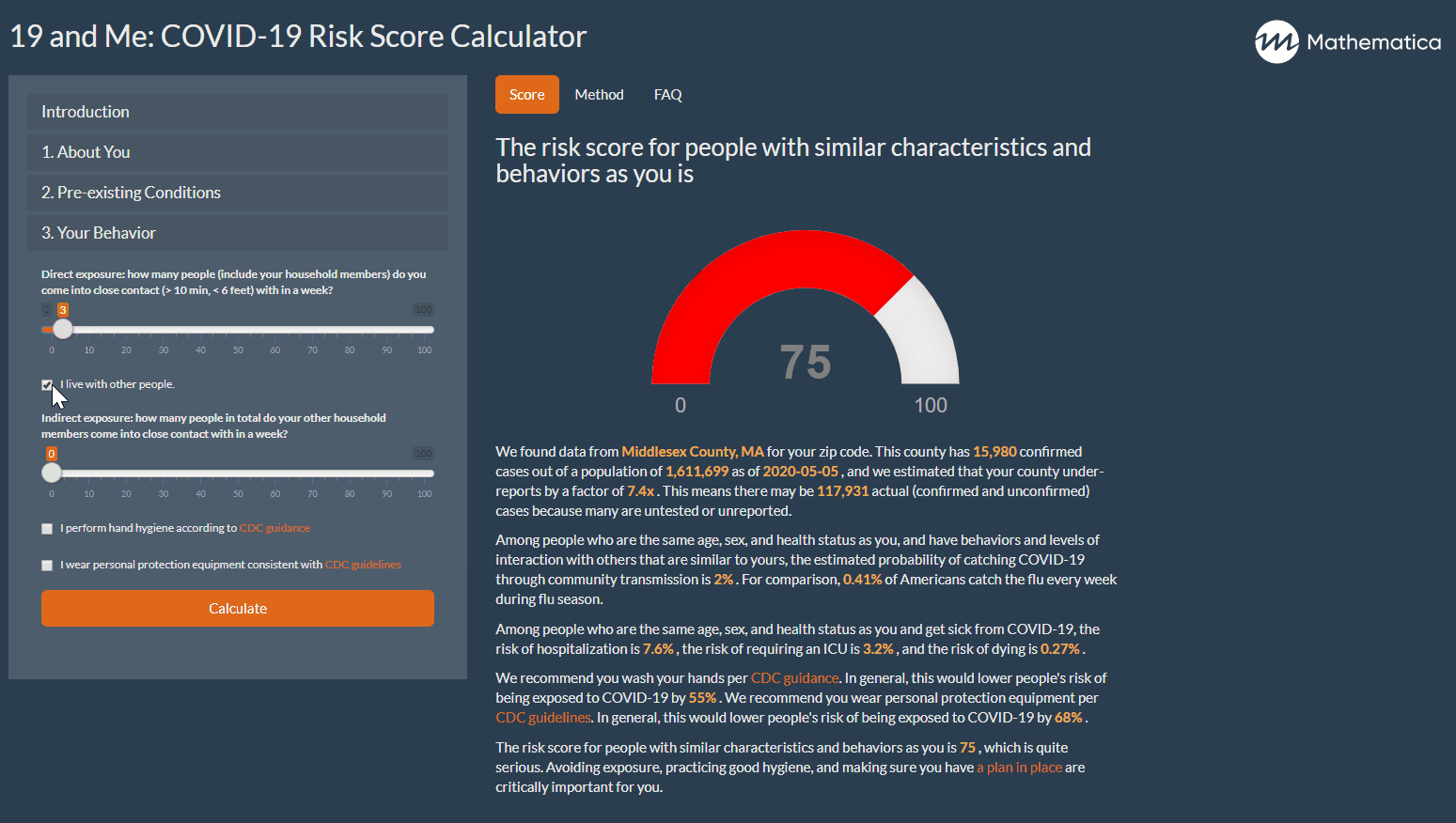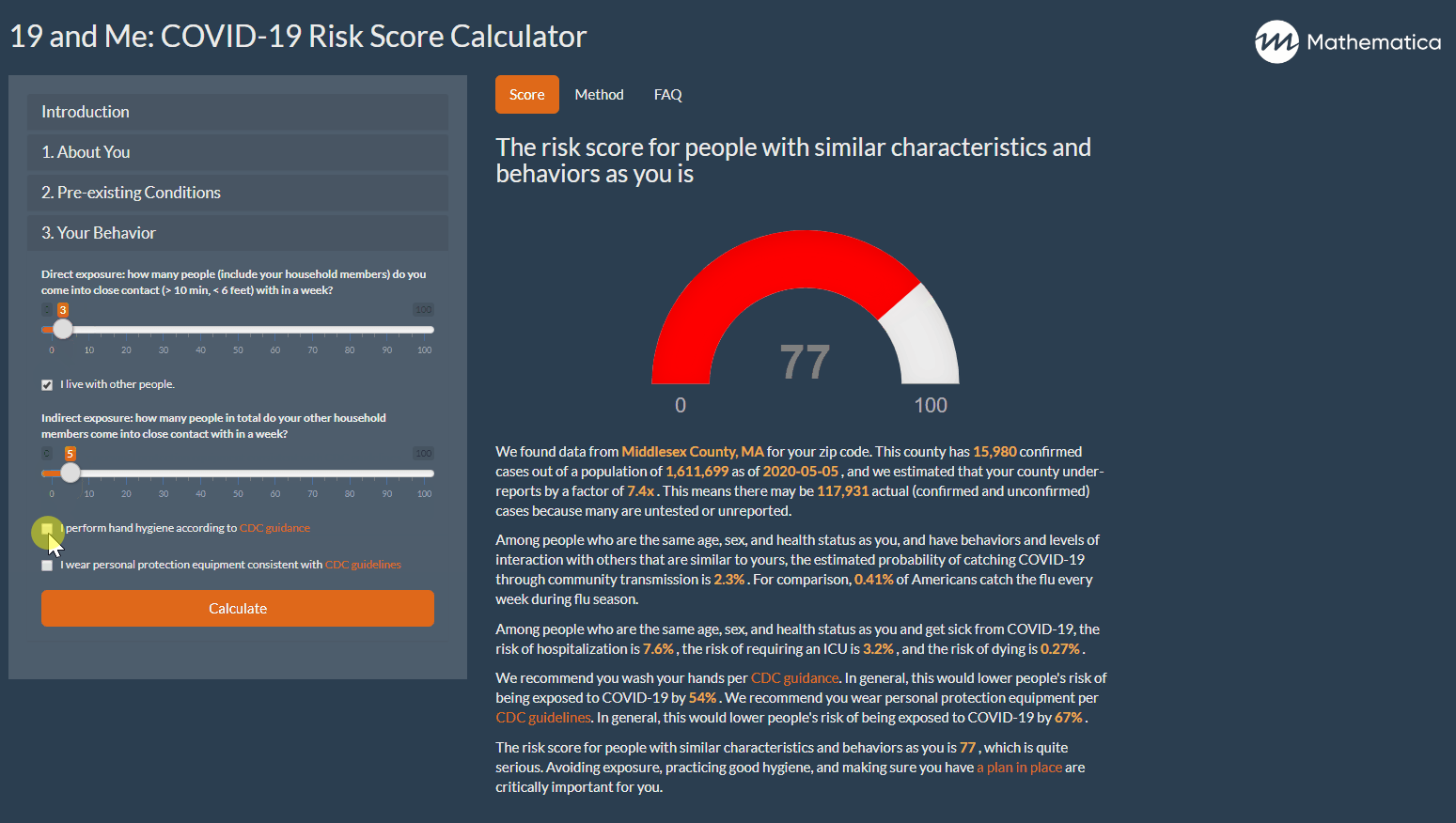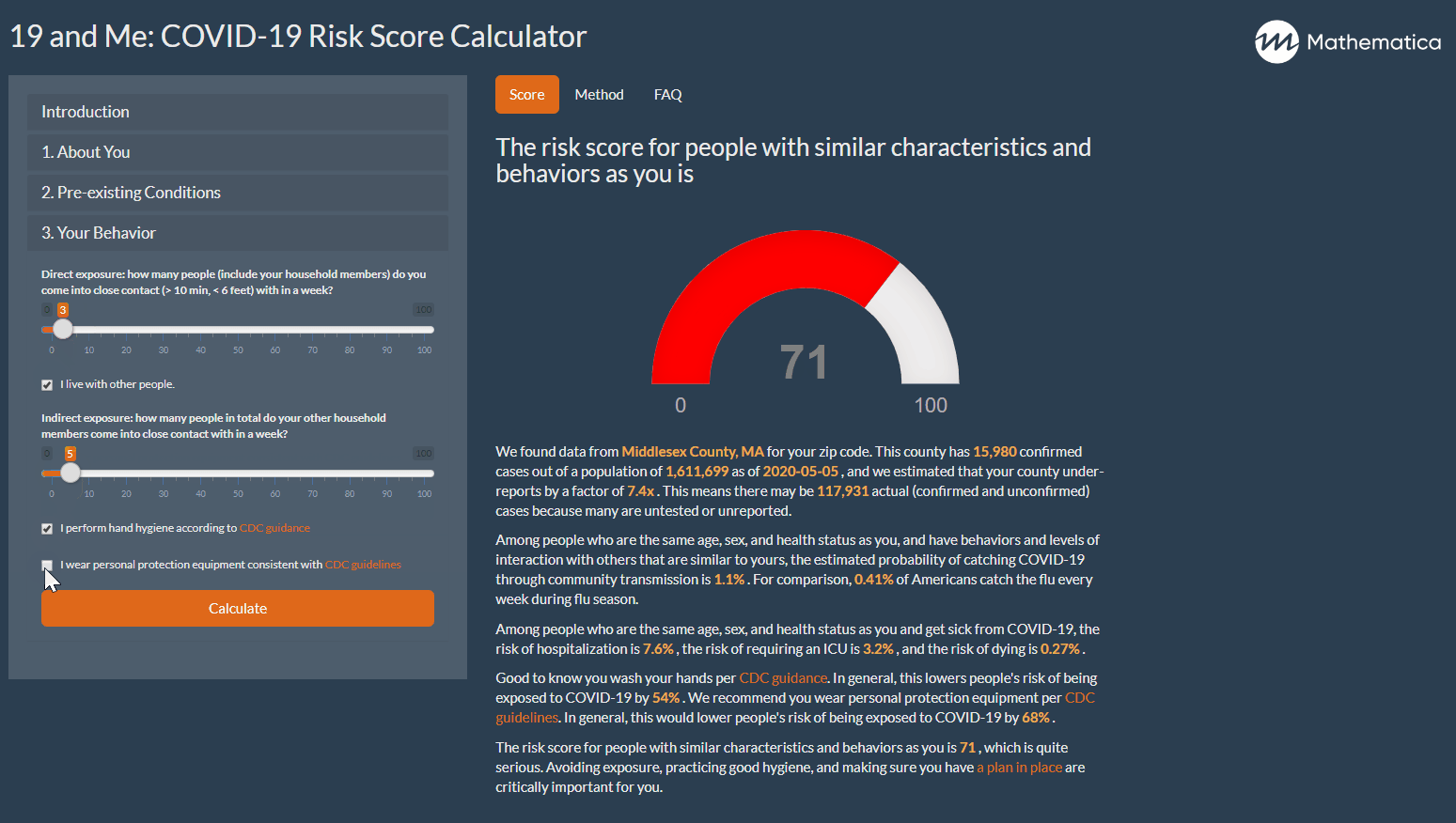


19 And Me A Covid 19 Risk Calculator



A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine



Factors Associated With Increased Risk Of Patient No Show In Telehealth And Traditional Surgery Clinics Journal Of The American College Of Surgeons



File Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Svg Wikimedia Commons



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
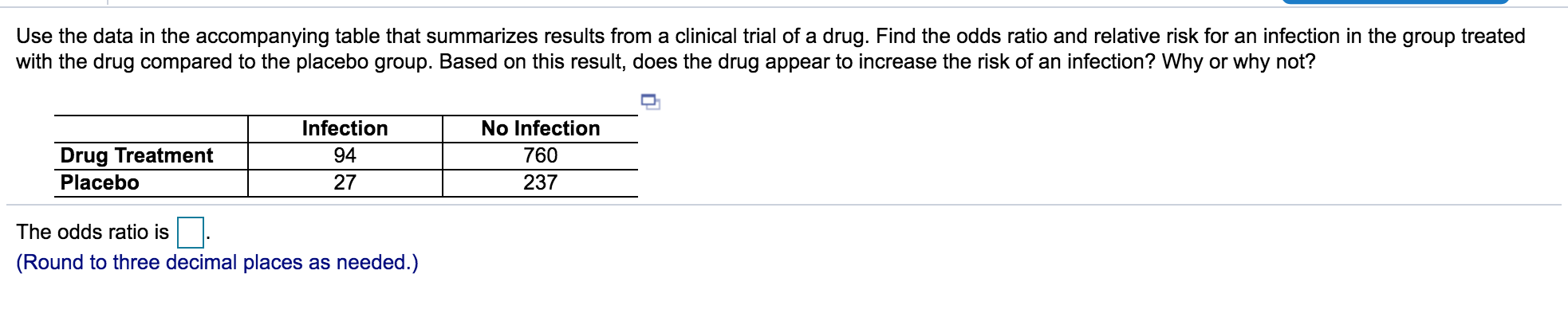


Solved Part A Calculate The Odds Ratio Part B Calculate Chegg Com



Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube
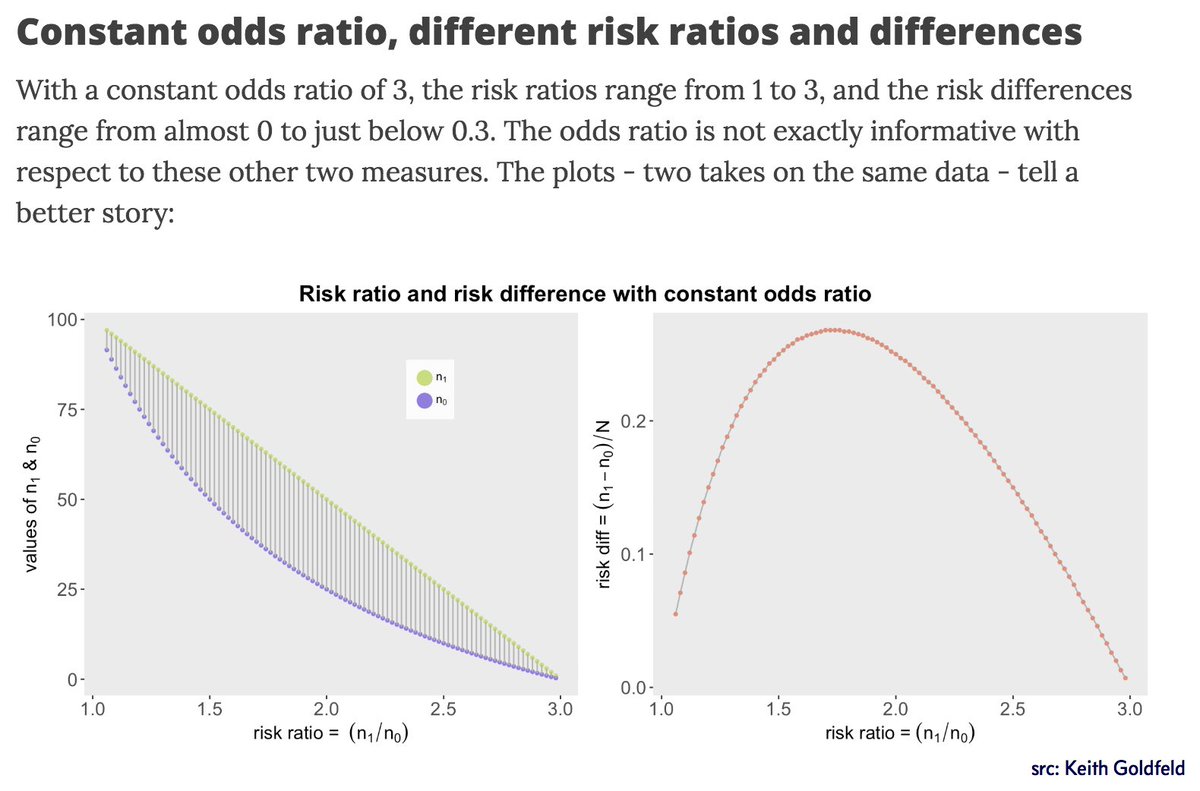


Mara Averick As Someone Who Asks For Odds Ratios And Relative Risk At The Vet I This Post How The Odds Ratio Confounds A Brief Study In A



Leeds Vs Southampton Betting Odds Offers And Tips Get Risk Free Bet On Premier League Clash Plus 25 1 Bet Builder



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿